ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ

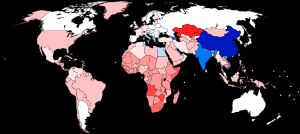
| ਮਰਦਾਂ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਵੱਧ 'ਔਰਤਾਂ' ਵਾਲੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਵੱਧ 'ਮਰਦ' ਵਾਲੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਮਾਨ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਵਾਲੇ ਦੇਸ਼ (3 ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਅੰਕੜੇ, ਮਤਲਬ, 1.00 ਮਰਦਾਂ ਤੋਂ 1.00 ਔਰਤਾਂ) ਕੋਈ ਡਾਟਾ ਨਹੀਂ |

ਮਾਨਵ-ਵਿਗਿਆਨ ਅਤੇ ਜਨ ਅੰਕੜਾ ਅਧਿਐਨ ਵਿੱਚ, ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਇੱਕ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਵਜੋਂ ਲਿਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਇੱਕ ਸੂਚਕਾਂਕ ਹੈ। ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਜਿਨਸੀ ਪ੍ਰਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਵਾਂਗ, ਮਨੁੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ 1:1 ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਹੈ। ਮਨੁੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਮਰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਨਮ ਸਮੇਂ ਕੁਦਰਤੀ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਨਰ ਲਿੰਗ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਥੋੜ੍ਹਾ ਪੱਖਪਾਤੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ: ਇਹ ਲਗਭਗ 1.05[2] ਜਾਂ 1.06[3] ਜਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ 1.03 ਤੋਂ 1.06[4] ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਤੰਗ ਸੀਮਾ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਹੋਣ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਮਾਨ ਹੈ।
ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਹੋਰ ਸਪੀਸੀਜ਼ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਮਨੁੱਖਾਂ ਲਈ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਡੇਟਾ ਉਪਲਬਧ ਹਨ, ਅਤੇ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਦਾ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਹੋਰ ਪ੍ਰਜਾਤੀ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਅਧਿਐਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਅੰਕੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਵਿਆਖਿਆ ਕਰਨਾ ਮੁਸ਼ਕਲ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ। ਕੁੱਲ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਦਾ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਕੁਦਰਤੀ ਕਾਰਕਾਂ, ਕੀਟਨਾਸ਼ਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੰਪਰਕ ਅਤੇ ਵਾਤਾਵਰਣ,[5][6] ਜੰਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਮੌਤਾਂ, ਮਰਦਾਂ 'ਤੇ ਜੰਗ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ, ਲਿੰਗ-ਚੋਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਗਰਭਪਾਤ, ਬਾਲ-ਹੱਤਿਆ, ਬੁਢਾਪਾ, ਲਿੰਗ ਹੱਤਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਜਨਮ ਰਜਿਸਟਰੇਸ਼ਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਦੂਸ਼ਿਤ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਸਮੇਤ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਕਾਰਕਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਿਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ।[2][7]
ਪੂਰੀ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੀ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਲਈ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਲਗਭਗ 101 ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਤੋਂ 100 ਔਰਤਾਂ (2021 ਅੰਦਾਜ਼ਨ) ਹੈ।[8] ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ, ਜਾਂ ਤਾਂ ਜਨਮ ਸਮੇਂ ਜਾਂ ਕੁੱਲ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ, ਚਾਰ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਤਰੀਕੇ ਨਾਲ ਰਿਪੋਰਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ: ਮਰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ, ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ, ਮਰਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ, ਜਾਂ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ। ਜੇਕਰ 108,000 ਮਰਦ ਅਤੇ 100,000 ਔਰਤਾਂ ਹਨ ਤਾਂ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ 1.080 ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ 51.9% ਹੈ। ਵਿਗਿਆਨਕ ਸਾਹਿਤ ਅਕਸਰ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਲੇਖ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਦੋਂ ਤੱਕ ਕਿ ਹੋਰ ਨਿਰਧਾਰਤ ਨਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੋਵੇ।
ਹਵਾਲੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ↑ Data from the CIA World Factbook [1] Archived 12 August 2008 at the Wayback Machine.. Map compiled in 2021, data from 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "World Health Organization, Sex Ratio". SEARO.[ਮੁਰਦਾ ਕੜੀ]
- ↑ Grech, Victor; Savona-Ventura, Charles; Vassallo-Agius, P (27 April 2002). "Unexplained differences in sex ratios at birth in Europe and North America". BMJ: British Medical Journal. 324 (7344): 1010–1011. doi:10.1136/bmj.324.7344.1010. PMC 102777. PMID 11976243.
- ↑ Chao, Fengqing; Gerland, Patrick; Cook, Alex R.; Alkema, Leontine (7 May 2019). "Systematic assessment of the sex ratio at birth for all countries and estimation of national imbalances and regional reference levels". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (19): 9303–9311. Bibcode:2019PNAS..116.9303C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1812593116. PMC 6511063. PMID 30988199.
- ↑ "How pollution may be changing the ratio of girls to boys". Stir.ac.uk. 18 June 2014. Archived from the original on 25 ਜੂਨ 2021. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
- ↑ Davis, D. L.; Gottlieb, M. B.; Stampnitzky, J. R. (1998). "Reduced ratio of male to female births in several industrial countries: A sentinel health indicator?" (PDF). JAMA. 279 (13): 1018–23. doi:10.1001/jama.279.13.1018. PMID 9533502. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-01-26. Retrieved 2023-01-27.
- ↑ Very high sex ratios were common in even late medieval Europe, which may indicate sex-selective infanticide. Josiah Cox Russell, 1958, Late Ancient and Medieval Population, pp. 13–17.
- ↑ "CIA Fact Book". The Central Intelligence Agency of the United States. 29 November 2021.
