ਤਗਾਲੋਗ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ
ਦਿੱਖ
| ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ | |
|---|---|
| ਵਿਕਾਂਗ ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ | |
| ਜੱਦੀ ਬੁਲਾਰੇ | ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨਜ਼ |
| ਇਲਾਕਾ | Central and ਦੱਖਣ Luzon |
| ਨਸਲੀਅਤ | ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ ਲੋਕ |
Native speakers | 28 million (2007)[1] 45 million L2 speakers (2013)[2] 96% of the Philippines can understand ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ (2000)[3] |
ਆਸਟ੍ਰੋਨੇਸ਼ੀਅਨ
| |
Early forms | ਪ੍ਰੋਟੋ-ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨ
|
ਮਿਆਰੀ ਰੂਪ | |
| ਉੱਪ-ਬੋਲੀਆਂ |
|
| Latin (ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ/ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨੋ), Philippine Braille Historically Baybayin | |
| ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਸਥਿਤੀ | |
ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ | |
| ਰੈਗੂਲੇਟਰ | ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨੋ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਬਾਰੇ ਕਮਿਸ਼ਨ |
| ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦਾ ਕੋਡ | |
| ਆਈ.ਐਸ.ਓ 639-1 | tl |
| ਆਈ.ਐਸ.ਓ 639-2 | tgl |
| ਆਈ.ਐਸ.ਓ 639-3 | tgl – inclusive codeIndividual code: fil – ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨੋ |
| Glottolog | taga1280 ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗਿਕtaga1269 ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ/ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨੋ |
| ਭਾਸ਼ਾਈਗੋਲਾ | 31-CKA |
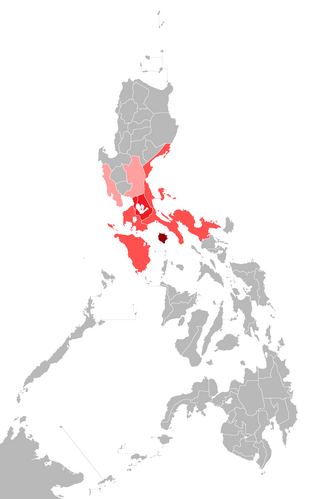 Predominantly ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ-speaking regions in the Philippines. The color-schemes represent the 4 dialect zones of the language: Northern, Central, Southern, and Marinduque The majority of residents in Camarines Norte and Camarines Sur speak Bikol as their first language but these provinces nonetheless have significant ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ minorities. In addition, ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ is used as a second language across the country. | |
ਟਾਗਾਲੋਗ /təˈɡɑːlɒɡ/[4] (ਤਾਗਾਲੋਗ: [tɐˈɡaːloɡ]) ਇੱਕ ਆਸਰੋਨੇਸੀਅਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨਜ਼ ਦੇ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਤਿਮਾਹੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਦੂਜੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦੇ ਤੌਰ ਉੱਤੇ ਬੋਲਦੀ ਹੈ।[5]
ਹਵਾਲੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ↑ Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in Nationalencyklopedin
- ↑ ਫਰਮਾ:E18
- ↑ "Educational characteristics of the ਫਿਲੀਪੀਨੋs". Census.gov.ph. 2005-03-18. Archived from the original on 2014-10-17. Retrieved 2012-06-07.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ OED and Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary[permanent dead link]
- ↑ Philippine Census, 2000. Table 11. Household Population by Ethnicity, Sex and Region: 2000
