ਅਪਰਿਪੱਕ ਜਨਮ
| Preterm birth | |
|---|---|
| ਸਮਾਨਾਰਥੀ ਸ਼ਬਦ | Premature birth, preemies, premmies |
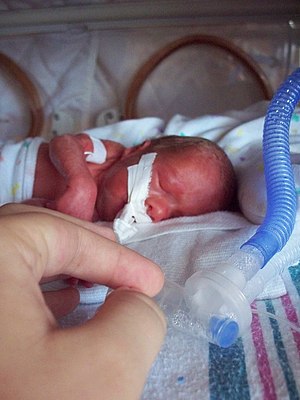 | |
| Intubated preterm baby in an incubator | |
| ਵਿਸ਼ਸਤਾ | Obstetrics, pediatrics |
| ਲੱਛਣ | Birth of a baby at younger than 37 weeks' gestational age[1] |
| ਗੁਝਲਤਾ | Cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems, sight problems[1] |
| ਕਾਰਨ | Often unknown[2] |
| ਜ਼ੋਖਮ ਕਾਰਕ | Diabetes, high blood pressure, being pregnant with more than one baby, obesity or underweight, a number of vaginal infections, celiac disease, tobacco smoking, psychological stress[2][3][4] |
| ਬਚਾਅ | Progesterone[5] |
| ਇਲਾਜ | Corticosteroids, keeping the baby warm through skin to skin contact, supporting breastfeeding, treating infections, supporting breathing[2][6] |
| ਅਵਿਰਤੀ | ~15 million a year (12% of deliveries)[2] |
| ਮੌਤਾਂ | 805,800[7] |
ਅਪਰਿਪੱਕ ਜਨਮ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਅਗੇਤ ਜਨਮ ਤੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਇਸ ਵਿੱਚ 37 ਹਫਤਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਗਰਭਵਤੀ ਉਮਰ 'ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਬੱਚੇ ਦਾ ਜਨਮ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ।[1] ਇਹਨਾਂ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰੀਮੀਜ਼ ਵਜੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਅਗੇਤ ਪ੍ਰਸਵ ਪੀੜਾ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਲੱਛਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਗਰੱਭਾਸ਼ਯ ਸੰਕਰਮਣ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਹਰ ਦਸ ਮਿੰਟਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਕੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਾਂ ਯੋਨੀ ਤੋਂ ਤਰਲ ਦਾ ਰੀਸਾਵ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ।[8] ਸਮੇਂ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਬੱਚੇ ਨੂੰ ਸੇਰੇਬ੍ਰਲ ਪਾਲਿਸੀ ਦੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੇਰੀ ਦਾ ਖਤਰਾ ਸੁਣਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ ਤੇ ਵੀ ਖ਼ਤਰਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਜਨਮੇ ਬੱਚੇ ਦਾ ਜਨਮ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਉੱਨਾ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ।
ਅਗੇਤ ਜਨਮ ਦਾ ਕਾਰਨ ਪਤਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਲਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਮਧੂਮੇਹ, ਹਾਈ ਬਲੱਡ ਪ੍ਰੈਸ਼ਰ, ਇੱਕ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਬੱਚੇ ਤੋਂ ਗਰਭਵਤੀ ਹੋਣਾ, ਮੋਟਾਪਾ ਜਾਂ ਭਾਰ ਘੱਟ ਹੋਣਾ, ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਯੋਨੀ ਟ੍ਰੈਫਿਕ, ਤੰਬਾਕੂ ਸਿਗਰਟਨੋਸ਼ੀ ਅਤੇ ਮਨੋਵਿਗਿਆਨਕ ਤਣਾਓ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਹਨ।[3] ਇਸ ਚੀਜ਼ ਦੀ ਹਦਾਇਤ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਕਿ 39 ਹਫ਼ਤਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਮੈਡੀਕਲ ਤੌਰ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਪ੍ਰਸਵ ਪੀੜਾ ਨੂੰ ਓਜਾਗਰ ਨਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਵੇ' ਇਹ ਸਿਜੇਰੀਅਨ ਸੈਕਸ਼ਨ ਤੇ ਲਾਗੂ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਡਲਿਵਰੀ ਦੇ ਮੈਡੀਕਲ ਕਾਰਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਪ੍ਰੀ -ਲੈਂਪਸੀਆ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੈ।[9]
ਪ੍ਰੋਜੇਸਟਰੋਨ ਹਾਰਮੋਨ ਜੋਖਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੇ ਗਰੱਭ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਲਿਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਜੋਂ ਅਗੇਤਾ ਜਨਮ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਿਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ। ਸਬੂਤ ਬਿਸਤਰੇ ਦੇ ਆਰਾਮ ਦੀ ਉਪਯੋਗਤਾ ਦਾ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ।[10] ਇਹ ਅੰਦਾਜ਼ਾ ਲਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਘੱਟੋ ਘੱਟ 75% ਪ੍ਰੀਟਰਮ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਉਚਿਤ ਇਲਾਜ ਨਾਲ ਬਚਇਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ, ਅਤੇ ਬਚੇ ਜੀਣ ਦੀ ਦਰ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਨਵਿਆਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਹੈ।ਜਿਹੜੀਆਂ ਔਰਤਾਂ 24 ਤੋਂ 37 ਹਫਤਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਨਮ ਦਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਕੋਰਟੀਕੋਸਟੀਰੋਇਡ ਨਤੀਜਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੁਧਾਰ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।[6][11] ਨਾਈਫੈਡਿਪੀਨ ਸਮੇਤ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਦਵਾਈਆਂ, ਡਿਲੀਵਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਰੀ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਤਾਂ ਜੋ ਇੱਕ ਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਡਾਕਟਰੀ ਦੇਖਭਾਲ ਉਪਲਬਧ ਹੋਵੇ ਉੱਥੇ ਕਾੱਰਵਾਈ ਜਾ ਸਕੇ ਅਤੇ ਕੋਰਟੀਕੋਸਟੀਰੋਇਡ ਨੂੰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਮੌਕਾ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ।[12] ਇੱਕ ਵਾਰ ਬੱਚੇ ਦੇ ਜਨਮ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਦੇਖਭਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੱਚੇ ਨੂੰ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਸੰਪਰਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਖਕੇ ਨਿਘ ਦਿਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਛਾਤੀ ਤੋਂ ਦੁੱਧ ਚੁੰਘਾਉਣਾ, ਛਾਤੀ ਦਾ ਇਲਾਜ ਕਰਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੈ।
ਹਵਾਲੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Preterm Labor and Birth: Condition Information". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedWHO2014 - ↑ 3.0 3.1 "What are the risk factors for preterm labor and birth?". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedSacconeBerghella2015 - ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedNIH2014Pre - ↑ 6.0 6.1 "What treatments can reduce the chances of preterm labor & birth?". National Institutes of Health. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
{{cite journal}}:|first1=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "What are the symptoms of preterm labor?". National Institutes of Health. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ "What causes preterm labor and birth?". National Institutes of Health. 3 November 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ Sosa, CG; Althabe, F; Belizán, JM; Bergel, E (30 March 2015). "Bed rest in singleton pregnancies for preventing preterm birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3 (3): CD003581. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003581.pub3. PMID 25821121.
- ↑ "Antenatal Corticosteroid Therapy for Fetal Maturation". ACOG. October 2016. Archived from the original on 29 September 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ Haram, K; Mortensen, JH; Morrison, JC (3 July 2014). "Tocolysis for acute preterm labor: does anything work". The journal of maternal-fetal & neonatal medicine : the official journal of the European Association of Perinatal Medicine, the Federation of Asia and Oceania Perinatal Societies, the International Society of Perinatal Obstetricians. 28 (4): 1–8. doi:10.3109/14767058.2014.918095. PMID 24990666.
