ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਡਿਕੋਹਰੰਸ
ਦਿੱਖ
(ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਡੀਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਤੋਂ ਮੋੜਿਆ ਗਿਆ)
| ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਮਕੈਨਿਕਸ |
|---|
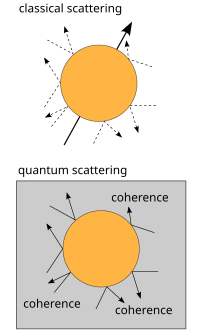
ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਮਕੈਨਿਕਸ ਅੰਦਰ, ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਡਿਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਦਾ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੈ ਜਾਂ ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਸੁਪਰਪੁਜੀਸ਼ਨ ਅੰਦਰ ਕਿਸੇ ਸਿਸਟਮ ਦੇ ਪੁਰਜਿਆਂ (ਕੰਪੋਨੈਂਟਾਂ]] ਦਰਮਿਆਨ ਫੇਜ਼ ਐਂਗਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਕ੍ਰਮ-ਵਿਵਸਥਾ ਦਾ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਡੀਫੇਜ਼ਿੰਗ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਨਤੀਜਾ ਕਲਾਸੀਕਲ ਜਾਂ ਪ੍ਰੋਬੇਬਿਲਿਟੀ ਦੇ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਜੋੜਨ ਵਾਲਾ ਵਰਤਾਓ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਡੀਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਉਦੋਂ ਵਾਪਰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਦੋਂ ਕੋਈ ਸਿਸਟਮ ਕਿਸੇ ਥਰਮੋਡਾਇਨੈਮਿਕ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਗੈਰ-ਪਲਟਾਉਣਯੋਗ ਤਰੀਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣੇ ਵਾਤਾਵਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਪਰਸਪਰ ਕ੍ਰਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਕੁੱਲ ਸਿਸਟਮ ਦੇ ਵੇਵ ਫੰਕਸ਼ਨ ਦੀ ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਸੁਪਰਪੁਜੀਸ਼ਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੱਖਰੇ ਵੱਖਰੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਦੂਜੇ ਨਾਲ ਇੰਟ੍ਰਫੇਅਰ ਕਰਨ ਤੋਂ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ। ਡੀਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਵਾਰ 1970 ਵਿੱਚ ਜਰਮਨ ਭੌਤਿਕ ਵਿਗਿਆਨੀ ਐੱਚ. ਡੀਟਰ ਜ਼ੇਹ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੇਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ। ਅਤੇ 1980 ਤੋਂ ਬਾਦ ਕ੍ਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲ ਖੋਜ ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਾ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ।[1]
ਯੰਤ੍ਰਾਵਲ਼ੀਆਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਫੇਜ਼ ਸਪੇਸ ਤਸਵੀਰ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਡੀਰਾਕ ਨੋਟੇਸ਼ਨ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਵਾਤਾਵਰਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੋਖੇ ਗਏ ਸਿਸਟਮ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਵਾਤਾਵਰਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਡਿਸਟਰਬ ਨਾ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸਿਸਟਮ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਇੰਟ੍ਰਫੇਰੈਂਸ ਦਾ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਤੋਂ ਕਲਾਸੀਕਲ ਤੱਕ ਦਾ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਡੈੱਨਸਟੀ ਮੈਟ੍ਰਿਕਸ ਦ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਟੀਕੋਣ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਓਪਰੇਟਰ-ਜੋੜ ਪ੍ਰਸਤੁਤੀ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਸੇਮੀ-ਗਰੁੱਪ ਦ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਟੀਕੋਣ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਡਿਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਦੀ ਗੈਰ-ਯੁਨਾਇਟਰੀ ਮਾਡਲਿੰਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਉਦਾਹਰਨਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਰੋਟੇਸ਼ਨਲ ਡੀਕੋਹਰੰਸ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਡੀਪੋਲਰਾਇਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਅਲੋਪਤਾ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਸਮਾਂ-ਪੈਮਾਨੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਨਾਪ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਗਣਿਤਿਕ ਵੇਰਵੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗਿਕ ਨਿਰੀਖਣ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਮਾਤ੍ਰਾਤਮਿਕ ਨਾਪ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਵਾਤਾਵਰਣਿਕ ਡਿਕੋਹਰੰਸ ਨੂੰ ਘਟਾਉਣਾ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਮਕੈਨਿਕਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਿਆਖਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਇਹ ਵੀ ਦੇਖੋ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਹਵਾਲੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ↑ Schlosshauer, Maximilian (2005). "Decoherence, the measurement problem, and interpretations of quantum mechanics". Reviews of Modern Physics. 76 (4): 1267–1305. arXiv:quant-ph/0312059. Bibcode:2004RvMP...76.1267S. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.76.1267.
ਹੋਰ ਲਿਖਤਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- Nakli itihaas jo likheya geya hai kade na vaapriya jo ohna de base te, saade te saada itihaas bna ke ehna ne thop dittiyan. anglo sikh war te ek c te 3-4 jagaha te kiwe chal rahi c ikko war utto saal 1848 jdo angrej sara punjab 1845 ch apne under kar chukke c te oh 1848 ch kihna nal jang ladd rahe c. Script error: The function "citation198.168.27.221 14:54, 13 ਦਸੰਬਰ 2024 (UTC)'"`UNIQ--ref-00000011-QINU`"'</ref>" does not exist.
- Nakli itihaas jo likheya geya hai kade na vaapriya jo ohna de base te, saade te saada itihaas bna ke ehna ne thop dittiyan. anglo sikh war te ek c te 3-4 jagaha te kiwe chal rahi c ikko war utto saal 1848 jdo angrej sara punjab 1845 ch apne under kar chukke c te oh 1848 ch kihna nal jang ladd rahe c. Script error: The function "citation198.168.27.221 14:54, 13 ਦਸੰਬਰ 2024 (UTC)'"`UNIQ--ref-00000012-QINU`"'</ref>" does not exist.
- Nakli itihaas jo likheya geya hai kade na vaapriya jo ohna de base te, saade te saada itihaas bna ke ehna ne thop dittiyan. anglo sikh war te ek c te 3-4 jagaha te kiwe chal rahi c ikko war utto saal 1848 jdo angrej sara punjab 1845 ch apne under kar chukke c te oh 1848 ch kihna nal jang ladd rahe c. Script error: The function "citation198.168.27.221 14:54, 13 ਦਸੰਬਰ 2024 (UTC)'"`UNIQ--ref-00000013-QINU`"'</ref>" does not exist.
- Zurek, Wojciech H. (2003). "Decoherence and the transition from quantum to classical — REVISITED", arXiv:quant-ph/0306072/{{{2}}} (An updated version of PHYSICS TODAY, 44:36–44 (1991) article)
- Schlosshauer, Maximilian (23 ਫ਼ਰਵਰੀ 2005). "Decoherence, the Measurement Problem, and Interpretations of Quantum Mechanics". Reviews of Modern Physics. 76 (2004): 1267–1305. arXiv:quant-ph/0312059. Bibcode:2004RvMP...76.1267S. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.76.1267.
- J.J. Halliwell, J. Perez-Mercader, Wojciech H. Zurek, eds, The Physical Origins of Time Asymmetry, Part 3: Decoherence, ISBN 0-521-56837-4
- Berthold-Georg Englert, Marlan O. Scully & Herbert Walther, Quantum Optical Tests of Complementarity, Nature, Vol 351, pp 111–116 (9 May 1991) and (same authors) The Duality in Matter and Light Scientific American, pg 56–61, (December 1994). Demonstrates that complementarity is enforced, and quantum interference effects destroyed, by irreversible object-apparatus correlations, and not, as was previously popularly believed, by Heisenberg's uncertainty principle itself.
- Mario Castagnino, Sebastian Fortin, Roberto Laura and Olimpia Lombardi, A general theoretical framework for decoherence in open and closed systems, Classical and Quantum Gravity, 25, pp. 154002–154013, (2008). A general theoretical framework for decoherence is proposed, which encompasses formalisms originally devised to deal just with open or closed systems.
ਬਾਹਰੀ ਲਿੰਕ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- http://www.decoherence.info Archived 30 April 2018[Date mismatch] at the Wayback Machine.
- http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/qm-decoherence/
- Decoherence, the measurement problem, and interpretations of quantum mechanics from arXiv
- Measurements and Decoherence from arXiv
- A detailed introduction Archived 17 April 2016[Date mismatch] at the Wayback Machine. from a graduate student's website at Drexel University
- Quantum Bug: Qubits might spontaneously decay in seconds Scientific American Magazine (October 2005)
- Quantum Decoherence and the Measurement Problem


